NormCyber threat bulletin: 20th March 2024

China Backed APT Observed Breaching Over 50 Organisations Worldwide

China Backed APT Observed Breaching Over 50 Organisations Worldwide

Researchers at Trend Micro have unveiled their discovery of a sophisticated campaign, active since 2022 and primarily targeting government organisations, with up to 70 organisations being impacted.
Attributed to the APT group Krahang, who are linked to China and are politically motivated, acting for cyber espionage purposes, they were observed to be sending spear phishing emails to deliver previously undetected back doors to exploit public facing servers.
Analysis of the attacks show the group often exploited access to government infrastructure to target other government entities. They used this infrastructure to host malicious payloads, proxy attack traffic, and send spear-phishing emails to government-related targets and leveraging compromised government email accounts. Not limited to enterprise networks, Krahang also pivoted to the victims private network by creating VPN servers on compromised public facing servers and conducting brute force attacks to obtain the victims user credentials. Once these credentials were maliciously obtained, the threat actor used these credentials to steal victims emails.
Trend Micro explained that in many of the attacks, the group scanned public facing servers with open-source tools to find targets with vulnerabilities to deploy web shells and gain a foothold in the victims networks.
The spear-phishing messages used by the group were designed to deceive victims into opening attachments or clicking on embedded URL links, which ultimately resulted in the deployment of a backdoor on the victim’s machine. Analysis of the backdoors uploaded on VirusTotal revealed that threat actors utilised geopolitical topics as bait.
Trend Micro summarised their research with the following statement “Earth Krahang abuses the trust between governments to conduct their attack.” This shows that even though this was a nation state backed threat actor with virtually unlimited funding, the fundamental vulnerability still mirrors other attacks; spear phishing. By utilising the Cyber Safety and Phishing module provided by NormCyber users can recognise potential phishing emails, by learning typical phishing tactics, signs of malicious links and what a phishing website may look like.
References:
Earth Krahang Exploits Intergovernmental Trust to Launch Cross-Government Attacks (trendmicro.com)
Microsoft Patch Tuesday March 2024
Another month, another Patch Tuesday. Microsoft has once again graced us with a whole host of security updates with their monthly patching, showcasing updates for 60 vulnerabilities including 18 that involve remote code execution flaws. This instalment only includes fixes to 2 critical vulnerabilities, which are Hyper-V remote code execution and denial of service flaws. It’s worth noting that no zero-days were disclosed in this month’s updates.
The Patch Tuesday updates can be broken down into multiple categories, which are listed below:
While there were no zero-day vulnerability fixes, there were still a few updates of note which will be listed below:
CVE-2024-21400
This vulnerability concerns privilege escalation via Microsoft Azure Kubernetes Service Confidential Container, which allowed users to elevate privileges and steal credentials. This vulnerability was scored 9.0 on the CVSS Scale. This vulnerability has been fixed with this latest patch. “An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could steal credentials and affect resources beyond the security scope managed by Azure Kubernetes Service Confidential Containers (AKSCC),” explains a Microsoft security advisory.
CVE-2024-26199
This fixed vulnerability also concerns privilege escalation exploitation, this time within Office, which allows any authenticated user to gain System privileges. It was stated that any authenticated user could trigger this vulnerability, with no admin or elevated privileges required. This vulnerability was assigned a CVSS Score of 7.8.
CVE-2024-20671
This fixed vulnerability could allow an authenticated attacker to prevent Microsoft Defender from starting on the device. Thankfully, this vulnerability’s patch will be rolled out by Windows Defender’s Antimalware platform updates which are automatically installed to Windows devices, making it almost impossible to miss. The version fixing this vulnerability is 4.18.24010.12. This vulnerability was assigned a CVSS Score of 5.5.
CVE-2024-21411
This vulnerability concerns Skype, and the vulnerability exploitation would allow attackers to remotely execute malicious code by sending a user a malicious link vi Skype’s Instant Messaging service. This vulnerability was assigned a CVSS Score of 8.8.
By utilising NormCyber’s Vulnerability Patch Management module, customers can ensure they are protected against vulnerabilities disclosed via vendor bug bounty programs.
References:
Microsoft March 2024 Patch Tuesday fixes 60 flaws, 18 RCE bugs (bleepingcomputer.com)
Security Update Guide – Microsoft
NVD – CVE-2024-21400 (nist.gov)
NVD – CVE-2024-26199 (nist.gov)
NVD – CVE-2024-20671 (nist.gov)
NVD – CVE-2024-21411 (nist.gov)
Unveiling Gitgub: Repositories acting as Launchpads for RisePro Info-Stealer
In an age where digital collaboration and code sharing are integral to software development, platforms like GitHub have become indispensable tools for developers worldwide. However, recent events and growing concerns have highlighted significant challenges regarding trust and security within GitHub repositories. This bulletin delves into the complexities surrounding trust issues on GitHub, exploring key deception tactics, potential risks, and strategies for mitigating threats in an environment where trust is paramount but not always guaranteed.
Recent cyber security research by G-Data and Splunk has shed light on a sophisticated threat campaign leveraging GitHub repositories to distribute the RisePro information stealer and other malicious payloads. Dubbed “gitgub,” this campaign involves repositories masquerading as providers of cracked software, enticing users with promises of free applications.
G-Data researchers discovered at least 13 repositories tied to the “gitgub” campaign, featuring README.md files adorned with green Unicode circles to mimic legitimate status indicators. All repositories shared the same download link, leading to “hxxps://digitalxnetwork[.]com/INSTALLER%20PA$$WORD%20GIT1HUB1FREE.rar.” Users had to unpack multiple layers of archives using the provided password “GIT1HUB1FREE” to access the “Installer_Mega_v0.7.4t.msi” installer.
This installer, using the password “LBjWCsXKUz1Gwhg,” then unpacked the next-stage “Installer-Ultimate_v4.3e.9b.exe,” posing as a 699 MB file to evade analysis tools such as IDA and ResourceHacker. However, the actual size was determined to be 3.43 MB, acting as a loader for the RisePro info-stealer (version 1.6).
Upon execution, the loader connects to a malicious domain and injects RisePro into system processes, RisePro, originally distributed via a pay-per-install malware downloader service called PrivateLoader, is designed to harvest sensitive information from infected devices and send it to predefined Telegram channels. The malware’s compact size and ability to inject into system processes like AppLaunch.exe or RegAsm.exe make it particularly elusive to analysis tools.
As of now, 17 repositories have been confirmed as being linked to the campaign and have subsequently been removed by GitHub:
It is believed that the campaign is still ongoing, and although tools have been developed to scan repositories related to the campaign they may sometimes fail, so always remain vigilant and be wary of GitHub pages looking similar to the one in Figure 1 below:
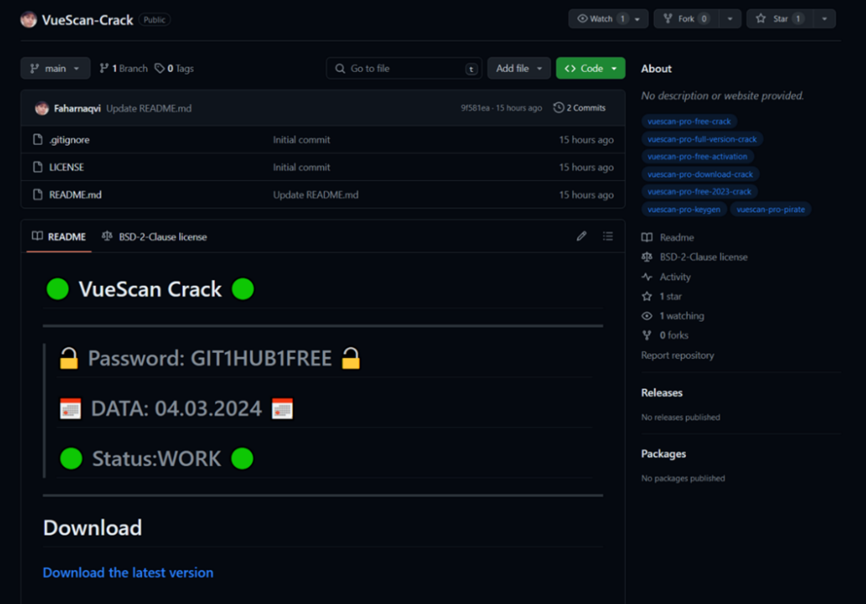
As the landscape of cyber threats continues to evolve, staying informed about emerging tactics and leveraging technical expertise becomes paramount in defending against sophisticated attacks targeting software repositories and unsuspecting users.
Alternatively, you could also leave it to the professionals of the industry, here are at NormCyber our Managed Threat Detection and Response package service provides near real-time security monitoring for your network, services and devices. Using telemetry feeds, threat intelligence feeds, use cases and play books, the NormCyber Security Operations Centre (SOC) identifies and isolates threats in near real-time, giving you peace of mind 24 hours a day, every day.
Resources
“GITGUB” MALWARE CAMPAIGN TARGETS GITHUB USERS WITH RISEPRO INFO-STEALER (securityaffairs.com)
Hackers Using Cracked Software on GitHub to Spread RisePro Info Stealer (thehackernews.com)
New HijackLoader Modular Malware Loader Making Waves in the Cybercrime World (thehackernews.com)
New info-stealer malware infects software pirates via fake cracks sites (bleepingcomputer.com)